Latin name
Heterodon platyrinos
Fast facts
Appearance
The Eastern Hognose Snake is a relatively stout snake with a thick neck and an upturned snout. The general coloring of this snake is highly variable, with prevailing colors being red, orange, olive, yellow, brown or gray. Jet black individuals are not rare, although typically the ground color is spotted with dark blotches. The undersurface is mottled and the underside of the tail is conspicuously lighter than the belly color. This is a snake whose undersurface is usually easy to see, given the snake's habit of turning over and "playing dead" when attacked.
Range
Overall Range
From New Hampshire south to Florida, and west to Minnesota, Nebraska, Kansas, Oklahoma and Texas.
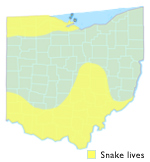
Range in Ohio
Northwestern counties near the western end of Lake Erie, and central and southern parts of the state.
Local Habitat
Dry, sandy areas; fields, upland hillsides with few trees, meadows.
Lifestyle
This diurnal snake is sometimes seen moving about across open land or sunning itself. When disturbed, the Hognose Snake flattens and spreads its head, puffs up its body, and hisses loudly. This behavior has given this snake several other common names: Puff Adder, Spreading Adder, Blow Viper. Occasionally an individual will strike, but typically with its mouth closed. If these antics fail to discourage its tormentor, a Hognose Snake will roll over onto its back, open its mouth allowing its tongue to hang out loosely, and it will remain limp and apparently lifeless even if picked up and handled by a person. During cold, winter weather the Hognose Snake burrows deeply into loose soil and hibernates.
More information
